Sirolimus Uses: Benefits, Risks & Medical Guidelines
Sirolimus is mainly used to prevent organ transplant rejection and manage some rare diseases.
It also helps reduce cancer risk and may slow aging.
In transplant patients, it lowers non-melanoma skin cancer risk by 51% and kidney cancer by 60%.
In this article, a complete guide to uses and their benefits.
What is Sirolimus?
Sirolimus is a macrolide compound originally discovered as an antifungal on Easter Island in 1972.
It was later found to have strong immunosuppressive and antiproliferative effects, leading to FDA approval in 1999 for use in kidney transplant patients.
Today, it is also used for rare conditions and studied for broader health benefits.
How Does Sirolimus Work in the Body?

Sirolimus works by blocking a pathway called mTOR (mechanistic target of rapamycin).
This pathway controls how cells grow, divide, and survive. Sirolimus binds with a protein called FKBP12 to form a complex that stops mTORC1, which:
- Slows down T-cell activity (immune response)
- Reduces protein production and cell growth
- Enhances autophagy, the body’s cell-cleaning process
Related: Does Viagra Really Make You Harder?
Is Sirolimus an Immunosuppressant?
Yes, sirolimus is a selective immunosuppressant.
It helps prevent organ rejection by calming the immune system.
Unlike other drugs, it does not block IL-2 production directly but instead blocks the response to IL-2, reducing T-cell and B-cell activity without harming kidney function.
What is Sirolimus Used to Treat? Approved Medical Uses
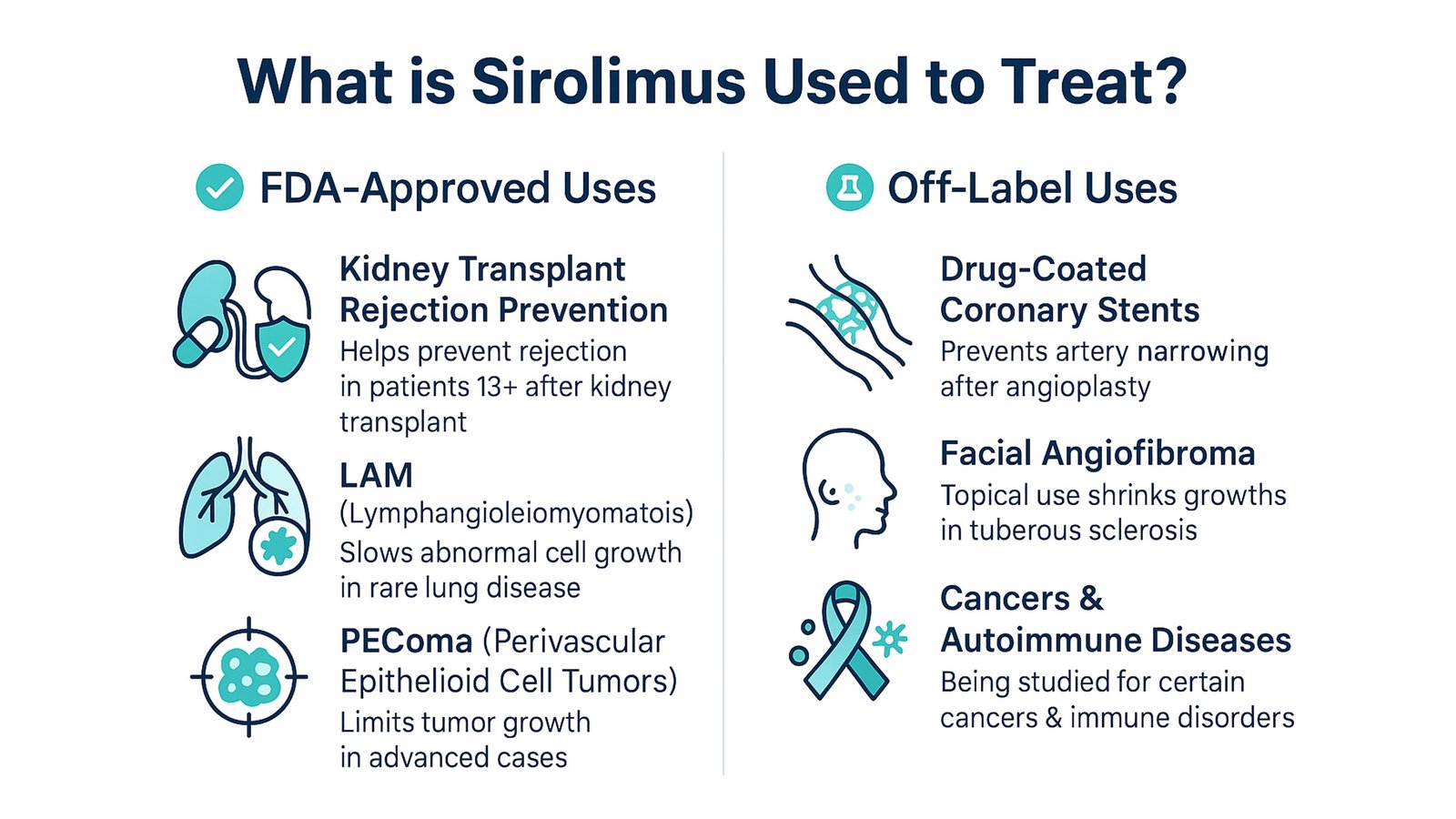
Sirolimus is FDA-approved for:
Kidney Transplant Rejection Prevention
Used in patients 13 years and older, sirolimus helps prevent rejection after a kidney transplant. It works by calming the immune system without damaging the kidneys.
LAM (Lymphangioleiomyomatosis)
This rare lung disease affects women. Sirolimus helps slow abnormal cell growth and supports better lung function.
PEComa (Perivascular Epithelioid Cell Tumors)
In advanced PEComa cases, sirolimus is used to limit tumor growth by targeting specific pathways in the body.
Off-label Uses
- Drug-coated Coronary Stents: Sirolimus prevents artery narrowing after angioplasty.
- Facial Angiofibroma: Topical use helps shrink skin growths in tuberous sclerosis patients.
- Cancers and Autoimmune Diseases: Still being studied, but shows promise for blood cancers and immune disorders.
Related: 11 Common Sildenafil Side Effects You Must Know
Sirolimus Benefits for Health
Sirolimus provides more than just immune suppression:
For Transplant Patients
- Excellent graft survival: Kidney transplant patients show a 99.51% graft survival rate
- Reduced nephrotoxicity: Safer for kidneys than calcineurin inhibitors
For Cancer Prevention
- 51% lower risk of non-melanoma skin cancer
- 60% lower risk of kidney cancer
- 29% overall reduction in cancer rates vs. other immunosuppressants
For LAM Patients
- Improves lung function and quality of life
- Slows disease progression significantly
For Anti-Aging Potential
- Extends lifespan in mice by 12%
- Promotes cellular cleanup and reduces inflammation
Related: Generic Ivermectin: Side Effects Guide
Risks and Safety of Sirolimus

Like all medications, sirolimus has risks:
Common Side Effects (≥20%)
- Swelling (42.3%)
- Protein in urine (37.5%)
- High cholesterol and triglycerides
- Mouth ulcers, diarrhea, low blood cell counts
Serious Risks
- Lung inflammation (pneumonitis – 9.7%)
- Poor wound healing
- Higher infection risk
- Rare blood vessel problems (TMA)
- Possible increase in prostate cancer risk (IRR = 1.85)
Drug Interactions & Precautions
- Avoid with CYP3A4 drugs (e.g., ketoconazole, rifampin)
- Don’t consume grapefruit juice
- Not for liver/lung transplants or pregnancy unless necessary
Related: Venous Leak Erectile Dysfunction: Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis & Treatment Options
Conclusion
Sirolimus is a valuable medication for transplant care and rare disease management.
It offers unique benefits like cancer prevention and potential anti-aging effects.
While side effects exist, they can be managed with proper monitoring by your doctor.
FAQs
Q: How long does sirolimus take to work?
A: It takes about 6 days to reach steady levels for transplant care. LAM patients may see lung benefits in 6–12 months.
Q: Can sirolimus be stopped suddenly?
A: No. Always taper off under medical supervision.
Q: Can I get vaccines while on sirolimus?
A: Avoid live vaccines. Inactivated vaccines may work but may be less effective.
Q: Is it safe during pregnancy?
A: Use only if the benefits outweigh risks. It’s classified as Category C.
Q: How is sirolimus monitored?
A: Through regular blood tests (trough levels, kidney/liver function, lipids, blood count).
Sources:

Aug 12, 2025
Generic and brand name medications work the same. They treat the same conditions and use the same main ingredients. The big difference is price generics…
VIEW DETAILSAug 12, 2025
Fenbendazole is not considered safe for human use according to the FDA and major medical bodies. While some people are…
Aug 12, 2025
Semaglutide helps people lose weight by lowering hunger and making them feel full for longer. It’s available as a weekly…

